Core Java Basics: Quick Reference
9 min readAug 6, 2021

Function:
- A block of code that performs a task.
void sendEmail(){
...
}- camelNamingConvention
Class:
- A container for related functions.
public class Main {
public void main() {
...
}
}- PascalNamingConvention
Compilation Process:

- JRE: Java Runtime Environment
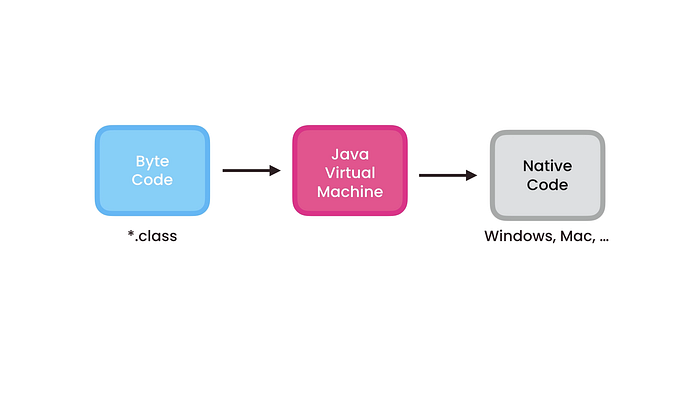
avinashbest/ $ javac Main.javaavinashbest/ $ cd ..src/ $ java com.avinashbest.Main
Interesting Facts about Java:
- Java was developed by James Gosling in 1995.

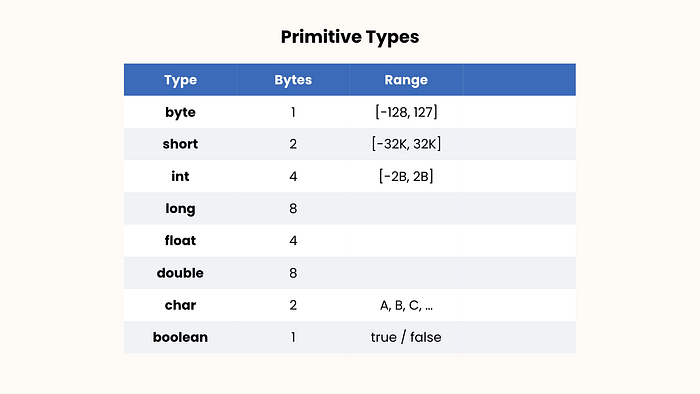
Types:
- Primitive: for storing simple values, like numbers, characters, booleans.
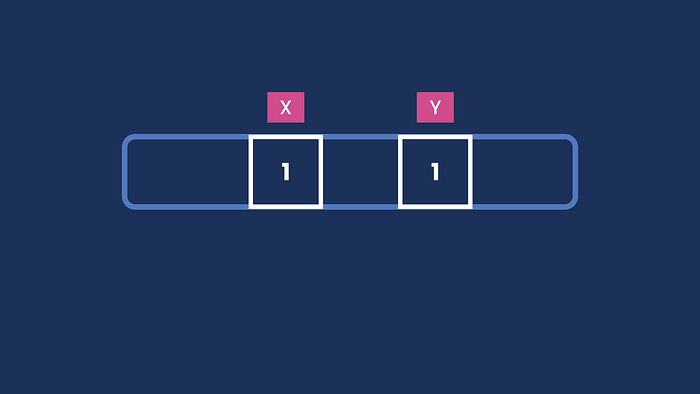
- How primitive types are stored in memory.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
}
}
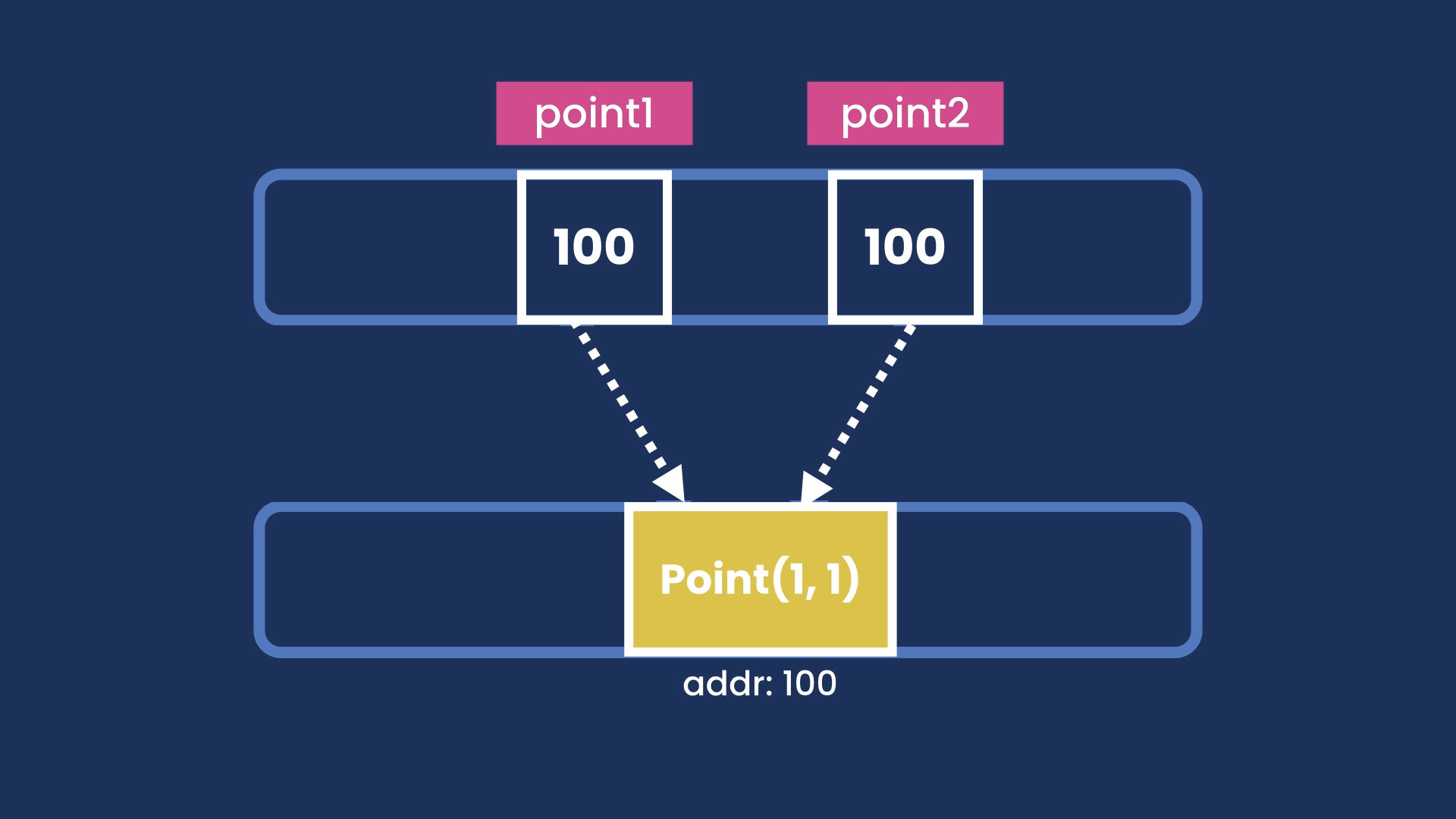
- Reference: for storing complex objects, like date, mail, message
- How primitive types are stored in memory.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point point1 = new Point(1, 1);
Point point2 = point1;
}
}
}
String:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String message = "Hello World" + "!!"; System.out.println(message.endsWith("!!"));
System.out.println(message.startsWith("!!"));
System.out.println(message.length());
System.out.println(message.indexOf("l"));
System.out.println(message.indexOf("sky"));
System.out.println(message.replace("!", "*"));
System.out.println(message.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT));
System.out.println(message.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT));
System.out.println(message.trim()) ; /*To remove unnecessary space.*/ /*NOTE: IN JAVA, ALL THE METHOD WHICH PERFORM OPERATION ON STRING RETURNS A NEW STRING.*/
/*ALL THE STRING IN JAVA ARE IMMUTABLE*/
System.out.println(message);
}
}
Escape Sequence:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) {
String message1 = "Hello \"Avinash\"";
String message2 = "C:\\Windows\\...";
String message3 = "C:\nWindows\n...";
String message4 = "C:\tWindows\t..."; System.out.println(message1);
System.out.println(message2);
System.out.println(message3);
System.out.println(message4);
}
}
Arrays:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] number = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
System.out.println(number.length);
Arrays.sort(number);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(number));
}
}Multi-Dimensional Arrays:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] numbers = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(numbers));
}
}
Arithmetic Expressions:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = 10 + 3;
System.out.println(result);
result = 10 - 3;
System.out.println(result);
result = 10 / 3;
System.out.println(result);
result = 10 * 3;
System.out.println(result);
result = 10 % 3;
System.out.println(result);
}
}Increment / Decrement Operator:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1;
x++;
System.out.println(x);
++x;
System.out.println(x); x = 1;
int y = x++; // post-increment
System.out.println(x + "\t" + y);
y = ++x; //pre-increment
System.out.println(x + "\t" + y); x += 2; //x = x + 2
System.out.println(x);
x -= 2; //x = x - 2
System.out.println(x);
x *= 2; //x = x * 2
System.out.println(x);
x /= 2; //x = x / 2
System.out.println(x);
x %= 2; //x = x % 2
System.out.println(x);
}
}
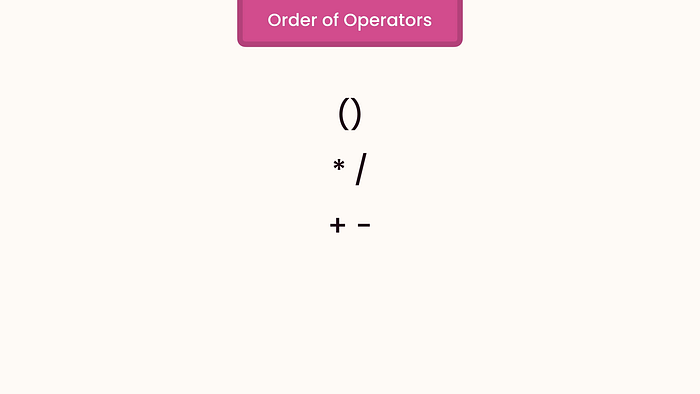
Order of Operations:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = (10 + 3) * 2;
}
}Type Casting:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*Implicit Casting*/
/*byte > short > int > long > float > double*/
short x = 1;
int y = x + 2;
System.out.println(y);
/*Explicit Casting*/
double a = 1.1;
int b = (int) (a + 2);
System.out.println(b);
/*Parsing String in Integer*/
String str = "123";
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(str));
}
}The Math Class:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.round(1.2F));
System.out.println(Math.round(1.2));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(1.2));
System.out.println(Math.floor(1.2));
System.out.println(Math.max(200, 300));
System.out.println(Math.min(200, 300));
System.out.println(Math.random());//by default return a doubleType random number b/w 0 to 1
System.out.println(Math.round(Math.random() * 100));
System.out.println((int) (Math.random() * 100));
}
}Formatting Numbers:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NumberFormat currency = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
String result = currency.format(123456.789);
System.out.println(result); NumberFormat percent = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
String percentage = percent.format(0.1);
System.out.println(percentage); System.out.println(NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(134343134313L));
}
}
Reading Input:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Age: ");
byte age = scanner.nextByte();
System.out.print("Name: ");
// String name = scanner.next(); //returns the next token
String name = scanner.nextLine().trim(); //returns next line
System.out.println("You are " + age);
System.out.println("Your name " + name);
}
}Mortgage Calculator — v1.0:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final byte MONTHS_IN_YEAR = 12;
final byte PERCENT = 100; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Principal: ");
int principal = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.print("Annual Interest Rate: ");
float annualInterest = scanner.nextFloat();
float monthlyInterest = annualInterest / PERCENT / MONTHS_IN_YEAR; System.out.print("Period (Years): ");
byte years = scanner.nextByte();
int numberOfPayments = years * MONTHS_IN_YEAR; /*calculating mortgage*/
double mortgage = principal * (monthlyInterest * Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments)
/ (Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments) - 1)); System.out.println("Mortgage: " + NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(mortgage));
}
}
Comparison Operators:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
System.out.println(x == y);
System.out.println(x != y);
System.out.println(x > y);
System.out.println(x >= y);
System.out.println(x < y);
System.out.println(x <= y);
}
}Logical Operators:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int temperature = 22;
boolean isWarm = temperature > 20 && temperature < 30;
System.out.println(isWarm); boolean hasHighIncome = true;
boolean hasGoodCredit = true;
boolean hasCriminalRecord = false;
boolean isEligible = (hasGoodCredit || hasHighIncome) && !hasCriminalRecord;
System.out.println(isEligible);
}
}
if-statement:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int temperature = 32;
if (temperature > 32) {
System.out.println("It's a hot day");
System.out.println("Drink water");
} else if (temperature > 20) {
System.out.println("Beautiful day");
} else {
System.out.println("Cold day");
}
/*Simplifying if-statement*/
int income = 120_000;
boolean hasHighIncome;
if (income > 100_000) {
hasHighIncome = true;
} else {
hasHighIncome = false;
}
/*Above Expression can be simplified by professional be like*/
int income = 120_000;
boolean hasHighIncome = income > 100_000;
}
}Ternary Operators:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int income = 120_000;
String className;
if (income > 100_000) {
className = "First";
} else {
className = "Economy";
}
/*Simplification can be done as*/
income = 120_000;
className = "Economy";
if (income > 100_000) {
className = "First";
}
/*More Simplification can be done using Ternary Operator*/
income = 120_000;
className = (income > 100_000) ? "First" : "Economy";
}
}Switch Statements:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String role = "admin";
switch (role) {
case "admin":
System.out.println("You're an admin");
break;
case "moderator":
System.out.println("You're a moderator");
break;
default:
System.out.println("You're a guest");
} if (role == "admin") {
System.out.println("You're an admin");
} else if (role == "moderator") {
System.out.println("You're a moderator");
} else {
System.out.println("You're a guest");
}
}
}
Exercise: FizzBuzz:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Number: ");
int number = scanner.nextInt(); boolean moduloFive = (number % 5) == 0;
boolean moduloThree = (number % 3) == 0; if (moduloFive && moduloThree) {
System.out.println("FizzBuzz");
} else if (moduloFive) {
System.out.println("Fizz");
} else if (moduloThree) {
System.out.println("Buzz");
} else {
System.out.println(number);
}
}
}
Loops in Java:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
/*FOR LOOPS*/
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello, Java!");
}
/*WHILE LOOPS: USED WHEN DON'T KNOW HOW MANY TIMES WE NEED TO EXECUTE CODE*/
int i = 0;
while (i < 5) {
System.out.println("Hello, Java!");
i++;
} String input = "";
while (!input.equals("quit")) {
System.out.print("Input: ");
input = scan.next().toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT);
System.out.println(input);
}
/*DO-WHILE LOOPS: SIMILAR TO WHILE-LOOP BUT IT EXECUTES ATLEAST 1 TIME*/
do {
System.out.print("Input: ");
input = scan.next().toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT);
System.out.println(input);
} while (!input.equals("quit"));
}
}
Break & Continue Keywords:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = ""; while (true) {
System.out.print("Input: ");
input = scan.next().toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT);
if (input.equals("pass")) {
continue;/*moves control to the beginning of the loop*/
}
if (input.equals("quit")) {
break;/*break out of the loop*/
}
System.out.println(input);
}
}
}
Mortgage Calculator — v2.0:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final byte MONTHS_IN_YEAR = 12;
final byte PERCENT = 100; int principal;
float annualInterest;
float monthlyInterest;
byte years;
int numberOfPayments; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) {
System.out.print("Principal ($1K - $1M): ");
principal = scanner.nextInt();
if (principal >= 1000 && principal <= 1_000_000) {
break;
}
System.out.println("Enter a value between $1000 and $1,000,000");
} while (true) {
System.out.print("Annual Interest Rate (1% - 30%): ");
annualInterest = scanner.nextFloat();
if (annualInterest >= 1 && annualInterest <= 30) {
monthlyInterest = annualInterest / PERCENT / MONTHS_IN_YEAR;
break;
}
System.out.println("Enter a value between 1 and 30");
} while (true) {
System.out.print("Period (1 Years- 30 Years): ");
years = scanner.nextByte();
if (years >= 1 && years <= 30) {
numberOfPayments = years * MONTHS_IN_YEAR;
break;
}
System.out.println("Enter a value between 1 and 30"); }
/*calculating mortgage*/
double mortgage = principal * (monthlyInterest * Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments)
/ (Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments) - 1)); System.out.println("Mortgage: " + NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(mortgage));
}
}
Creating Methods:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String message = greetUser("Avinash", "Kumar");
System.out.println(message);
} public static String greetUser(String firstName, String lastName){
return "Hello " + firstName + " " + lastName;
}
}
Mortgage Calculator — v3.0:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int principal = (int) readNumber("Principal ($1K - $1M): ", 1000, 1_000_000);
float annualInterest = (float) readNumber("Annual Interest Rate (1% - 30%): ", 1, 30);
byte years = (byte) readNumber("Period (1 Years- 30 Years): ", 1, 30); double mortgage = calculateMortgage(principal, annualInterest, years);
System.out.println("Mortgage: " + NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(mortgage));
} public static double readNumber(String prompt, double min, double max) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double value;
while (true) {
System.out.print(prompt);
value = scanner.nextDouble();
if (value >= min && value <= max) {
break;
}
System.out.println("Enter a value between " + min + " and " + max);
}
return value;
} public static double calculateMortgage(int principal, float annualInterest, byte years) {
final byte MONTHS_IN_YEAR = 12;
final byte PERCENT = 100; float monthlyInterest = annualInterest / PERCENT / MONTHS_IN_YEAR;
short numberOfPayments = (short) (years * MONTHS_IN_YEAR); return principal * (monthlyInterest * Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments)
/ (Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments) - 1));
}
}
Mortgage Calculator — Clean Code:
public class Main {
final static byte MONTHS_IN_YEAR = 12;
final static byte PERCENT = 100; public static void main(String[] args) {
int principal = (int) readNumber("Principal ($1K - $1M): ", 1000, 1_000_000);
float annualInterest = (float) readNumber("Annual Interest Rate (1% - 30%): ", 1, 30);
byte years = (byte) readNumber("Period (1 Years- 30 Years): ", 1, 30); printMortgage(principal, annualInterest, years); printPaymentSchedule(principal, annualInterest, years);
} private static void printPaymentSchedule(int principal, float annualInterest, byte years) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("PAYMENTS SCHEDULE:");
System.out.println("------------------");
for (short month = 1; month <= years * MONTHS_IN_YEAR; month++) {
double balance = calculateBalance(principal, annualInterest, years, month);
System.out.println(NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(balance));
}
} private static void printMortgage(int principal, float annualInterest, byte years) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("MORTGAGE");
System.out.println("--------");
double mortgage = calculateMortgage(principal, annualInterest, years);
System.out.println("Monthly Payments: " + NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(mortgage));
} public static double readNumber(String prompt, double min, double max) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double value;
while (true) {
System.out.print(prompt);
value = scanner.nextDouble();
if (value >= min && value <= max) {
break;
}
System.out.println("Enter a value between " + min + " and " + max);
}
return value;
} public static double calculateBalance(int principal, float annualInterest, byte years, short numberOfPaymentsMade) {
float monthlyInterest = annualInterest / PERCENT / MONTHS_IN_YEAR;
short numberOfPayments = (short) (years * MONTHS_IN_YEAR); double balance = principal * (Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments)
- Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPaymentsMade))
/ (Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments) - 1); return balance;
} public static double calculateMortgage(int principal, float annualInterest, byte years) {
float monthlyInterest = annualInterest / PERCENT / MONTHS_IN_YEAR;
short numberOfPayments = (short) (years * MONTHS_IN_YEAR); return principal * (monthlyInterest * Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments)
/ (Math.pow(1 + monthlyInterest, numberOfPayments) - 1));
}
}
Refactoring
- Changing the structure of the code without changing its behaviour.
- Keep your methods short
- Extract repetitive patterns
- Extract highly related statements
Types of Errors
- Compile — Time Errors
- Run — Time Errors
Running a Java Archive (.jar) in local:
$ java -jar file-name.jarThank You!

Credits:
- CodeWithMosh - https://codewithmosh.com/
- Avinash Kumar - https://github.com/avinashbest/core-java
